The structure of topological spaces and the structure of simplicial sets look similar to each other at first sight so we might think it would be easy to embed simplicial sets in topological spaces. It turns out that simplicial sets can be embed in topological spaces but we have to go via linear algebra which, at first sight, doesn't feel intuitive.
Where does that come from?
Geometric Realisation Example
| Lets take this very simple graph consisting of two lines glued together at one end. |
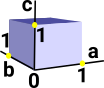
One posibility is to make the verticies open sets like this: {a} , {b} and {c}.
Also make the lines open sets like this: {a,b} and {b,c}.
But these open sets: {a} , {b} , {c} , {a,b} and {b,c} do not form a topological space, for example, they do not include {a,b,c}.
To make this into a topological space we need to make each of the verticies into a seperate dimension. So 'a' is now a continuous line represented by a Real number between 0 and 1. Same for 'b' and 'c'. This cube is now a topological space. |
 |
Topological Space and Simplicial Sets (Geometric Realisation)
Topological spaces have some nice properties, they have the concept of nearness in the most general way. However topological spaces have some quite stringent requirements, geometric realisation gives use a way to embed any CW complexes or simplicial set as a topological space.
A first thought for how to embed simplicial sets in topological spaces might be to equate each simplex with an open set, unfortunately this won't work for the following reasons: |
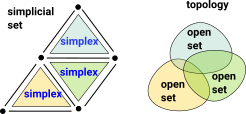 |
- Every union of simplices in a CW complex is not a simplex but unions of open sets must be open sets.
- Every pair of simplices don't necessarily have an intersection.
There is a way to canonically get a topological space from a simplicial complex, this requires a much higher dimensional space so its not very intuitive. For instance, to encode a graph (2D complex), each vertex in the graph needs to have its own dimension in the topological space.
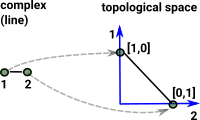
Here we want to encode a complex with two points and a line. We embed this in 2 dimensional Euclidean space (and therefore topological space).
Each of the points is now a vector in its own dimension, these are [1,0] and [0,1] and they are the basis vectors. The line is a straight line between these basis vectors, parameterised by t like this { (1-t)*[1,0]+t*[0,1] | t |
 |
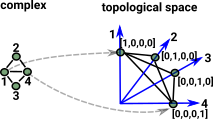 |
A more complex graph gives a lot more dimensions which makes visualising the topological space harder. |
For more information about geometric realisation see the page here.
An n-simplex is homeomorphic to a closed n-dimensional ball - discrete topology (see paper on arxiv here).
The intersection of any two simplices of X, if non-empty, is a face of each them. So every intersection of simplices in a CW complex is also a simplex, although every pair of simplices don't necessarily have an intersection and, every union of simplices in a CW complex is not a simplex (so not directly equivalent to a topological space?).
Representation Theory for Simplicial Sets
see wiki.
The Yoneda Embedding (see page here)
| Assume a category C where the objects are sets of points and the morphisms are total functions. |  |
allows us to represent categories in set.
 |
The opposite category to this Cop has the same objects but the morphisms are opposite which means elements in the domain may map to zero or multiple elements in the codomain. This corresponds to face maps and degeneracy maps in simplicial sets. |
| Adding an additional point (origin) allows each point to be represented as a vector. Then the morphism is represented by a matrix. |  |
More about representation theory for simplicial sets on page here.
Geometric Realisation and Delta Complexes
There is a close connection between geometric realisation and delta complexes.
When we embed a simplicial set or cell complex into a topological space we have a dimension for each vertex and the vertex is represented by a vector from 0 to 1 in that dimension. We can do the same for lines, triangles ... There in now a linear mapping between vertices, lines, triangles... (that is a matrix). So a topological shape is now represented by a sequence of matrices.
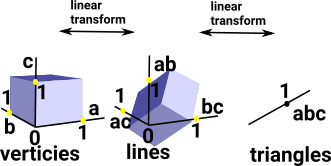
More information:
- page about geometric realisation here
- page about delta complexes here
